Contents
In today’s logistics and transportation industry, fleet safety and operational efficiency are more important than ever. With regulations tightening and insurance costs climbing, U.S. fleet managers are seeking tools that do more than just track vehicles – they want insights that improve driver performance, reduce risk, and simplify compliance.
This is where AI dash cams integrated with fleet management software come into play. These systems are transforming how fleets operate by combining visual data with telematics analytics, creating a powerful, centralized hub for real-time decision-making.
In this guide, we’ll explore how AI dash cams work, their integration with fleet management systems, and the benefits, challenges, and best practices for fleets across the United States.
The Role of AI Dash Cams in Modern Fleets
What Are AI Dash Cams?
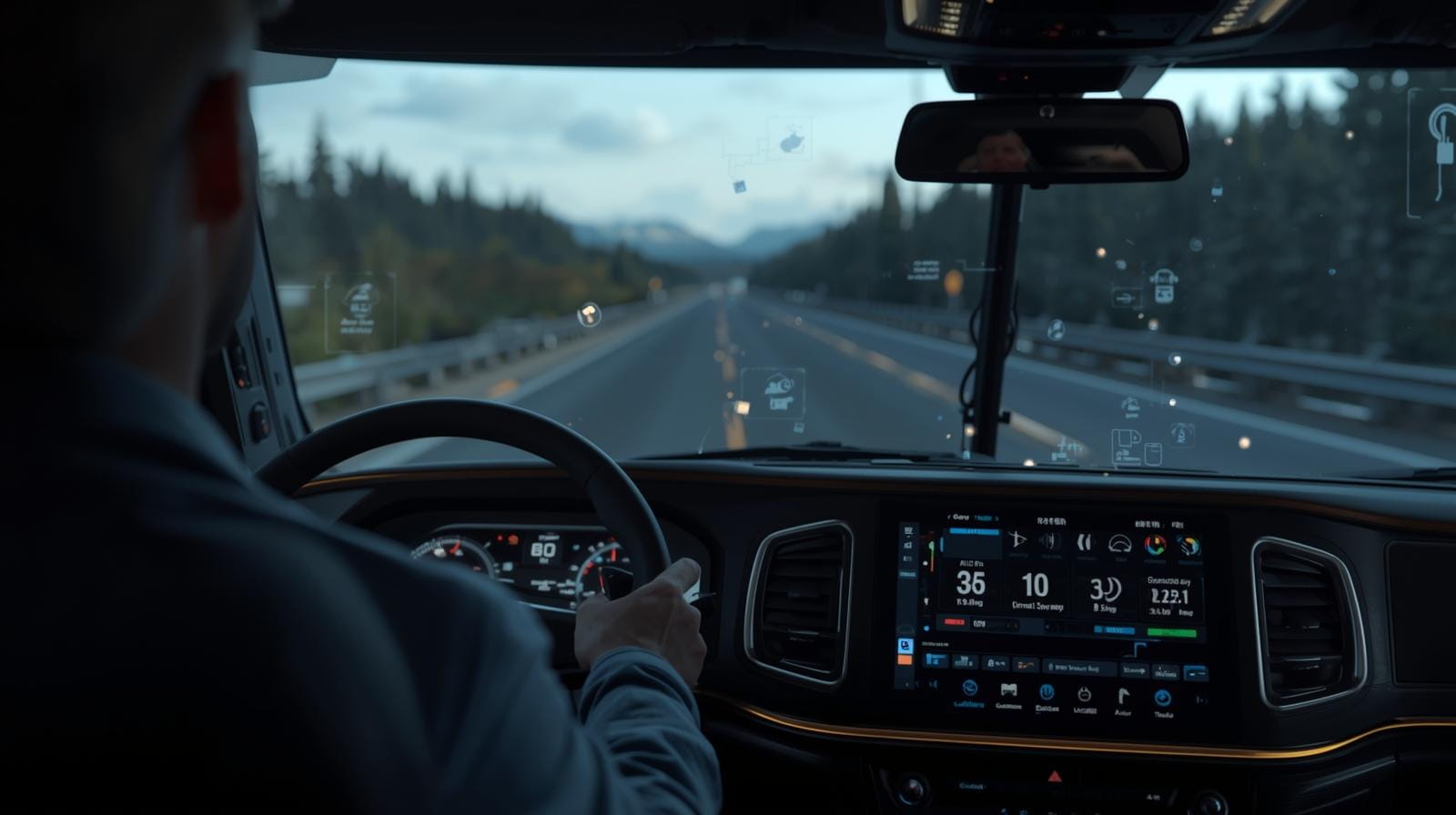
An AI dash cam goes far beyond simple video recording. Unlike traditional cameras, AI-enabled devices use machine learning to detect risky behaviors and events in real time – like hard braking, tailgating, distracted driving, or lane drifting.
Some advanced dash cams also feature dual-facing lenses, capturing both the road and the driver cabin, allowing for comprehensive event analysis.
Why U.S. Fleets Are Adopting AI Dash Cams
For fleet operators in the United States, these systems are a response to:
- FMCSA safety initiatives that demand better driver behavior tracking.
- Soaring insurance premiums, where video evidence can reduce liability and fraud claims.
- Litigation risks, with video serving as critical evidence in crash investigations.
According to a 2023 report by the American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI), fleets using AI dash cams saw a 22% reduction in preventable accidents within the first year of implementation.
Fleet Management Software: A Quick Overview
Fleet management software provides a centralized platform to monitor, control, and optimize fleet operations. Core features typically include:
- Vehicle tracking: Real-time GPS location of assets.
- Driver performance analytics: Insights into speeding, idling, and HOS compliance.
- Maintenance scheduling: Proactive service alerts to prevent breakdowns.
- Regulatory compliance: Support for FMCSA rules like HOS logging and DVIRs.
The real power emerges when these platforms integrate with AI dash cams, turning raw video into actionable operational data.
How AI Dash Cams Integrate with Fleet Management Systems
- Seamless Data Sharing
Dash cam footage syncs directly with the fleet management platform, tagging videos with trip data, timestamps, and event types. For example, a harsh-braking event triggers an instant video clip, viewable alongside telematics data for context. - Real-Time Alerts & Notifications
Integration allows fleet managers to receive immediate alerts for critical incidents – like potential collisions, driver distraction, or camera tampering. This enables proactive intervention instead of post-incident reaction. - Driver Behavior Analytics
AI dash cams feed data into driver scorecards, giving fleet managers a 360-degree view of driving habits. Combined with telematics, this enables personalized coaching programs to reduce risky behaviors. - Compliance & Legal Documentation
In the U.S., DOT audits and FMCSA inspections require extensive documentation. Integrated systems store video and event logs securely, ensuring evidence is readily available for audits, investigations, and insurance claims.
Key Benefits of Integration
- Enhanced Safety – AI-powered dash cams help prevent accidents by detecting risks in real time, while fleet platforms make it easy to review incidents and coach drivers effectively.
- Insurance & Liability Protection – Video footage provides irrefutable evidence in insurance claims and legal disputes, often leading to faster claim resolutions and reduced settlements.
- Improved Fleet Efficiency – Combining video insights with telematics helps identify inefficient routes, reduce fuel consumption, and optimize resource allocation.
- Simplified Compliance – Integrated systems support FMCSA rules, providing automated logs, event footage, and records that make audits quicker and less stressful.
Challenges and Considerations for U.S. Fleets
- Data Privacy & Driver Acceptance – Drivers may resist dual-facing cameras due to privacy concerns. Successful fleets communicate the purpose – safety, not surveillance – and involve drivers in policy creation.
- Storage & Bandwidth – Video data is high-volume. Fleets must ensure adequate cloud storage and high-speed connectivity to handle uploads without disrupting operations.
- Integration Costs – Upfront costs can be steep, with dash cam hardware averaging $300–$600 per vehicle and monthly subscriptions ranging from $30–$60. However, ROI is often achieved through reduced accidents, lower insurance costs, and improved efficiency.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
- Set Clear Policies: Define how footage will be used (coaching vs. punitive measures).
- Train Drivers: Show how AI dash cams protect them from false claims and enhance safety.
- Regularly Review Data: Use analytics to adjust policies, improve routing, and reinforce safe driving practices.
- Start with a Pilot Program: Test with a small group before rolling out fleet-wide to fine-tune workflows.
FAQ
Are AI dash cams legal across all U.S. states?
Yes. AI dash cams are legal, but state laws may vary regarding dual-facing cameras and driver consent. Always review local regulations.
How long should fleet managers store dash cam footage?
Best practice is 90 days, but critical footage may be kept longer for litigation or insurance purposes.
Can AI dash cam data be used in insurance claims?
Absolutely. Video evidence is highly valuable in expediting claim settlements and defending against false claims.
What are the costs of integrating dash cams with fleet platforms?
Expect to pay $300–$600 per camera upfront and $30–$60 monthly per vehicle for subscription and cloud storage.
Which fleet management systems work best with AI dash cams?
Leading options include Samsara, Lytx, Verizon Connect, and Motive.