Contents
Hours-of-Service (HOS) regulations are a fundamental element in transportation safety, designed to prevent driver fatigue and reduce accident risk. Traditional compliance mechanisms, including manual logbooks and Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs), provide limited oversight and primarily retrospective analysis. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into HOS compliance monitoring introduces real-time observation, predictive violation detection, and automated alerts, transforming fleet management operations. This article examines the regulatory context, technological architecture, operational benefits, challenges, and future applications of AI-assisted HOS monitoring. Through case studies and practical examples, it demonstrates how AI enhances safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency while outlining the considerations necessary for successful implementation.
Driver fatigue remains a leading cause of accidents in the transportation sector. To mitigate this risk, regulatory authorities worldwide have established HOS rules that limit continuous driving hours, enforce mandatory rest periods, and govern duty schedules. Historically, compliance monitoring has relied on manual reporting and periodic inspections, which are prone to human error, falsification, and delayed enforcement.
ELD marked a significant advancement by automating the capture of driving hours, but these systems are largely reactive, identifying violations after they occur. AI-assisted systems address this gap by continuously monitoring driver activity, analyzing data in real-time, and generating predictive alerts that allow fleet managers to intervene before violations occur.
This article explores the architecture, advantages, and challenges of AI-driven HOS compliance, illustrating the transformative impact on operational safety, efficiency, and regulatory adherence.
Regulatory Framework of HOS Compliance
Overview of HOS Regulations
HOS regulations are designed to protect drivers and the public by limiting fatigue-related risks. In the United States, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) enforces regulations that allow a maximum of 11 hours of driving within a 14-hour on-duty period, requiring minimum off-duty intervals. Drivers are also restricted to 60 or 70 hours of driving over seven or eight days, depending on their operating schedules.
In Europe, Regulation EC 561/2006 mandates daily and weekly driving limits, minimum break periods, and maximum continuous driving times. Other jurisdictions have comparable frameworks, reflecting the global consensus on fatigue management and safety.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance carries both legal and operational consequences. Violations can result in fines, penalties, suspension of operations, and increased insurance premiums. Beyond legal implications, fatigue-induced incidents compromise driver safety, cargo integrity, and public trust. Effective HOS compliance monitoring is therefore essential for operational continuity, risk management, and fleet reputation.
Traditional HOS Monitoring Approaches
Manual Logbooks
Manual logbooks have been the standard method for HOS tracking. Drivers record duty status, driving hours, and rest periods on paper forms, which are later reviewed by fleet managers or regulatory inspectors. While inexpensive, this method is prone to inaccuracies, intentional falsification, and delayed enforcement, undermining compliance reliability.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs)
ELDs automatically capture driving time and duty status, providing accurate digital records and simplifying compliance reporting. Despite these advantages, ELDs primarily operate retrospectively, identifying violations after they occur rather than preventing them. They offer limited predictive insight into driver fatigue or operational inefficiencies.
Challenges in Real-Time Enforcement
Even with ELDs, real-time monitoring remains limited. Fleet managers often cannot detect violations or unsafe driving behavior until after the fact. Manual intervention is required to adjust schedules or enforce compliance, leading to operational delays and increased risk exposure. Real-time, AI-assisted systems aim to close this gap.
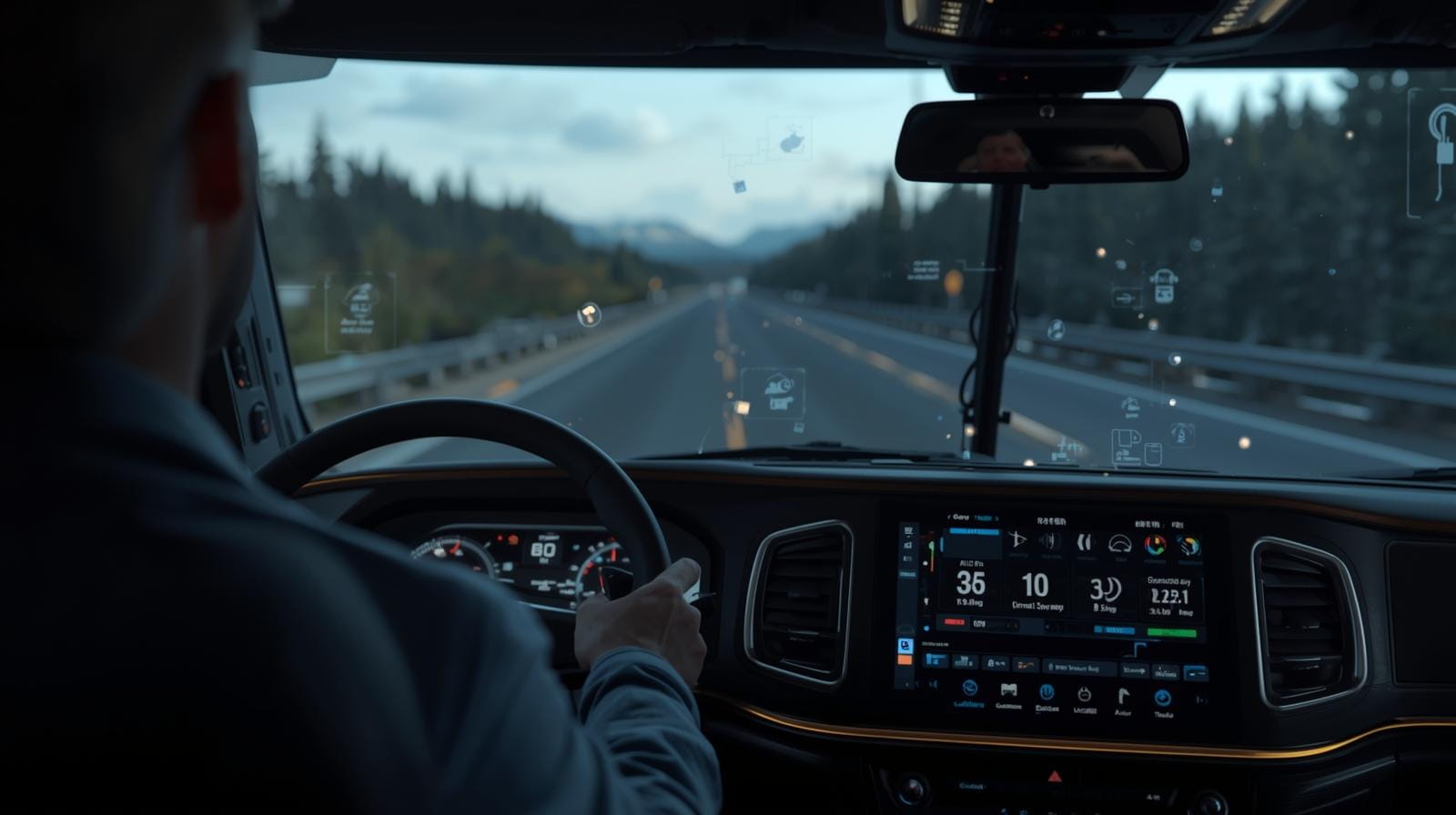
AI-Assisted HOS Compliance Monitoring
Role of AI in Fleet Management
Artificial Intelligence applies machine learning and predictive analytics to vast streams of fleet data. By analyzing patterns in driving behavior, rest intervals, and vehicle telematics, AI can detect anomalies, forecast HOS violations, and generate actionable alerts. This capability transforms compliance from a reactive to a proactive process.
Real-Time Data Acquisition
AI systems rely on a continuous stream of data from:
- Vehicle telematics (speed, engine status, mileage)
- GPS tracking (location, route adherence, traffic conditions)
- Driver inputs (duty status updates, manual corrections)
- Historical driving behavior and compliance records
This integrated data environment enables AI to monitor HOS adherence in real-time, identifying risks as they emerge and providing immediate notifications.
Predictive Compliance Models
Predictive algorithms assess cumulative driving hours, rest schedules, and historical driver patterns to forecast potential violations. These models can:
- Generate early warnings for drivers and fleet managers
- Recommend schedule adjustments to prevent violations
- Optimize routing to balance operational efficiency with regulatory compliance
By proactively managing compliance, fleets reduce violations and minimize fatigue-related risks.
Benefits of Real-Time AI Monitoring
Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
AI-driven monitoring ensures continuous adherence to HOS regulations. Automated alerts allow immediate corrective action, reducing violations, penalties, and audit exposure.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
By analyzing fatigue indicators, driving behavior, and operational patterns, AI systems detect potential hazards before they lead to incidents. Predictive alerts empower proactive intervention, improving driver safety and reducing accidents.
Operational Efficiency
Real-time monitoring enables dynamic scheduling and route optimization. Fleets can minimize downtime, reduce operational inefficiencies, and ensure timely deliveries while maintaining compliance.
Data-Driven Insights
AI systems generate detailed analytics, providing insights into systemic compliance patterns, driver behavior trends, and fleet performance. These insights inform strategic planning, risk management, and resource allocation.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Privacy and Security
Sensitive driver and operational data must be secured in compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Unauthorized access could compromise privacy and operational integrity.
Integration with Legacy Systems
AI monitoring may require integration with existing ELDs or fleet management software. Technical compatibility and implementation costs must be considered during deployment.
Accuracy and Reliability
Predictive models may generate false positives or fail in the absence of complete data. Continuous model training, validation, and monitoring are necessary to maintain accuracy.
Regulatory Acceptance
Automated alerts and predictive compliance recommendations must remain auditable and verifiable. Legal recognition of AI-assisted monitoring is evolving and requires transparent reporting and documentation.
Future Directions
- IoT and Blockchain Integration: Immutable HOS records can enhance regulatory trust and verification.
- Autonomous Scheduling: AI can dynamically adjust routes and rest schedules based on real-time conditions, reducing the reliance on manual oversight.
- Advanced Predictive Analytics: Incorporating biometrics, traffic patterns, and weather data can further enhance fatigue management and operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Evolution: Governments are exploring frameworks that formally recognize AI-assisted compliance monitoring, including automated reporting and predictive intervention.
FAQ
What is real-time HOS compliance monitoring?
Continuous observation of driving hours, rest periods, and duty status, enabling immediate detection and correction of potential violations.
How does AI enhance HOS compliance monitoring?
AI leverages predictive analytics and machine learning to detect anomalies, forecast violations, and provide actionable alerts in real-time.
Are AI-assisted monitoring systems legally recognized?
AI systems integrated with certified ELDs are typically accepted when auditability and verifiability are maintained.
What types of data are used for AI monitoring?
GPS, telematics, engine diagnostics, driver inputs, and historical compliance records.
Can AI predict driver fatigue?
Yes. Predictive models assess cumulative driving hours, rest intervals, and behavior patterns to flag fatigue risks before they manifest.
How do AI systems integrate with existing ELDs?
Through APIs and data ingestion protocols, allowing seamless integration while preserving regulatory compliance records.
What are the main operational benefits?
Reduced HOS violations, improved driver safety, optimized routing, enhanced scheduling, and actionable fleet analytics.
What challenges exist in AI monitoring implementation?
Data privacy, system integration, model accuracy, and regulatory recognition are key considerations.
AI-assisted real-time HOS compliance monitoring transforms fleet management by providing proactive, predictive oversight. By integrating telematics, predictive algorithms, and continuous monitoring, fleets can maintain regulatory compliance, reduce fatigue-related risks, optimize operations, and enhance overall safety. Adoption requires careful attention to regulatory alignment, system integration, data privacy, and accuracy validation. As AI technologies evolve and regulators adapt, AI-assisted monitoring is poised to become a critical standard in modern fleet operations.